|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Strategic
decisions & Working Capital (WC)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment
decisions |
|
|
Modes of diversification
: |
|
|
Inter-Organizational relationships
: |
|
|
|
|
|
Others : |
|
|
|
|
|
Long-Term
Financial decisions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment
analysis and decision |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What
is strategy ?
Definitions
of strategy
The strategy is
the way by which a firm fullfills
its mission and attains its objectives.
According to Brandenburger
& Stuart, the essence of strategy
lies in creating favorable asymmetries
between a firm and its rivals.
According to Barney
(1997), Strategy is a pattern of resource
allocation that enables firms to
maintain or improve their performances. A
good strategy neutralizes threats, exploits
opportunities, capitalizes on strenghts and/or
fixes weaknesses.
According to Porter,
a company can outperform rivals only if it
can establish a difference
that it can preserve.
- Create a unique
and valuable position, involving a
different set of activities
- Make trad-offs in competing
(e.g. choose what NOT to do)
Strategic
Management
Strategic management is the process
by which mission and objectives are chosen,
strategies decided and implemented through
policies and tactics.
Levels
of Strategy :
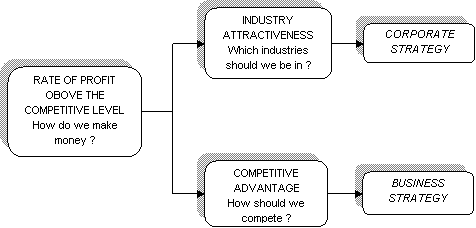
Corporate
Strategy defines the scope
of the firm in terms of industries and markets
in which it competes. In other words, Corporate
strategy answers the fundamental question
: WHICH IINDUSTRIES SHOULD WE BE IN
?
Corporate strategy
decisions include investment in diversification,
vertical integration, acquisitions, and new
ventures; the allocation of ressources between
the different businesses of the firm; and
divestments.
Business
Strategy is concerned with
how the firm competes within a particular
industry or market. What business or businesses
should we be in (corporate strategy) and within
each business : HOW SHOULD WE COMPETE
? (against competitors, for targeted
customers, to sustain performance). In single-business
firms there is no distinction between corporate
and business strategy.
The distinction
between Corporate Strategy & Business
Strategy corresponds to the organization
structure of the typical multibusiness corporation.
Corporate Strategy is the responsability of
the top management team, supported by corporate
strategy staff. Business Strategy is formulated
and implemented primarily by the individual
businesses (typically organized as divisions
or business units).
There is also a
third level of strategy :
functional strategy.
Functional Strategies are the elaboration
and implementation of business strategies
through individual functions such as production,
R&D, marketing, human resources and finance.
They are primarily the responsability of the
functional departments.
Strategy is not
a detailed plan or programm of instructions.
It is a unifying theme that
gives coherence and direction to the actions
and decisions of an organization.
The purpose is
to guide management decisions toward superior
performance (rate of profit above the competitive
level) through establishing competitive advantage.
Management's approach
to strategy must be dynamic, flexible and
innovative.
Four characteristics
of a successfull strategy :
-
Goals are
simple, consistent and long term (confused
objectives = failure)
-
Profound
understanding of the competitive environment
-
Objective
appraisal of resources
-
Effective
implementation
Sources :
Gaining and Soustaining Competitive Advantage, Jay. B. Barney, Addison-Wesley, 1997
Contemporary Strategic Analysis, Robert M. Grant, 3th edition, Blackwell, 1998
Strategic Management, Raphael Amit, Professor at Wharton University of Pennsylvania, US
ECOFINE.COM, Bernard Jaquier,
Professor in Economics and Finance, Lausanne, Switzerland,
2020
|
|
|